java递归算法的例子。
发布时间:2025-05-22 17:32:16 发布人:远客网络
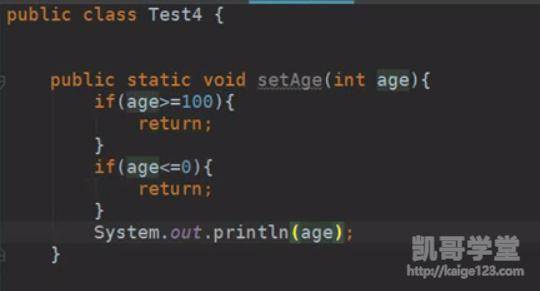
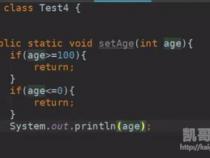
一、java递归算法的例子。
要求:给定一个数值,计算出它的阶乘值,例如5的阶乘为5*4*3*2*1
<span style="font-size:12px;">//利用递归实现一个数的阶乘值 private static BigDecimal getNum(BigDecimal inNum){ if(inNum.compareTo(BigDecimal.ONE)== 0){ return inNum;} return inNum.multiply(getNum(inNum.subtract(BigDecimal.ONE)));}</span>
(2)Fibonacci数列:1,1,2,3,5,8,13……
要求:找出数列中指定index位置的数值
<span style="font-size:12px;">//利用递归实现了Fibonacci数列 private static int fab(int index){ if(index== 1|| index== 2){ return 1;} else{ return fab(index- 1)+ fab(index- 2);}}</span>
<span style="font-size:12px;"><span style="white-space:pre;"></span>private static final String DISK_B="diskB";<span style="white-space:pre;"></span>private static final String DISK_C="diskC";<span style="white-space:pre;"></span>private static final String DISK_A="diskA";<span style="white-space:pre;"></span>static String from=DISK_A;<span style="white-space:pre;"></span> static String to=DISK_C;<span style="white-space:pre;"></span> static String mid=DISK_B;<span style="white-space:pre;"></span> public static void main(String[] args){<span style="white-space:pre;"></span> String input=JOptionPane.showInputDialog("please input the number of the disks you want me move.");<span style="white-space:pre;"></span> int num=Integer.parseInt(input);<span style="white-space:pre;"></span> move(num,from,mid,to);<span style="white-space:pre;"></span>}</span>
<span style="font-size:12px;">//利用递归实现汉诺塔 private static void move(int num, String from2, String mid2, String to2){ if(num== 1){ System.out.println("move disk 1 from"+ from2+" to"+ to2);} else{ move(num- 1, from2, to2, mid2); System.out.println("move disk"+ num+" from"+ from2+" to"+ to2); move(num- 1, mid2, from2, to2);}}</span>
要求:将输入的一个字符串中的所有元素进行排序并输出,例如:你给出的参数是"abc",
<span style="font-size:12px;"><span style="white-space:pre;"></span>public static void permute(String str){<span style="white-space:pre;"></span> char[] strArray= str.toCharArray();<span style="white-space:pre;"></span> permute(strArray, 0, strArray.length- 1);<span style="white-space:pre;"></span>}</span>
<span style="font-size:12px;">//利用递归实现,将输入的一个字符串中的所有元素进行排序并输出 public static void permute(char[] list, int low, int high){ int i; if(low== high){ String cout=""; for(i= 0; i<= high; i++){ cout+= list[i];} System.out.println(cout);} else{ for(i= low; i<= high; i++){ char temp= list[low]; list[low]= list[i]; list[i]= temp; permute(list, low+ 1, high); temp= list[low];
二、用java递归方法实现
1、递归做为一种算法在程序设计语言中广泛使用,是指函数/过程/子程序在运行过程中直接或间接调用自身而产生的重入现象。
2、递归算法一般用于解决三类问题:
1)数据的定义是按递归定义的。(Fibonacci(斐波那契)的函数)
2)问题解法按递归算法实现。(回溯)
3)数据的结构形式是按递归定义的。(树的遍历,图的搜索)
三、java中递归算法是什么怎么算的
1、Java递归算法是基于Java语言实现的递归算法。递归算法是一种直接或者间接调用自身函数或者方法的算法。递归算法实质是把问题分解成规模缩小的同类问题的子问题,然后递归调用方法表示问题的解。递归往往能给我们带来非常简洁非常直观的代码形式,从而使我们的编码大大简化,然而递归的思维确实跟我们的常规思维相逆的,通常都是从上而下的思维问题,而递归趋势从下往上的进行思维。
2、【2】在使用递归策略时,必须有一个明确的递归结束条件,称为递归出口。
3、【3】递归算法代码显得很简洁,但递归算法解题的运行效率较低。所以不提倡用递归设计程序。
4、【4】在递归调用的过程中系统为每一层的返回点、局部量等开辟了栈来存储。递归次数过多容易造成栈溢出等,所以一般不提倡用递归算法设计程序。
5、【5】在做递归算法的时候,一定把握出口,也就是做递归算法必须要有一个明确的递归结束条件。这一点是非常重要的。其实这个出口就是一个条件,当满足了这个条件的时候我们就不再递归了。
6、}
publicclassTestFactorial{
7、publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){
8、//TODOAuto-generatedmethodstub
9、Factorialfactorial=newFactorial();
10、System.out.println("factorial(5)="+factorial.fact(5));
11、}
代码执行流程图如下: