如何关闭Oracle11g数据库的审计功能
发布时间:2025-05-20 06:35:45 发布人:远客网络
一、如何关闭Oracle11g数据库的审计功能
在oracle11g中,数据库的审计功能是默认开启的(这和oracle10g的不一样,10g默认是关闭的),
oracle11gR2的官方文档上写的是错的,当上说default是none,而且是审计到DB级别的,这样就会
1.如果审计不是必须的,可以关掉审计功能;
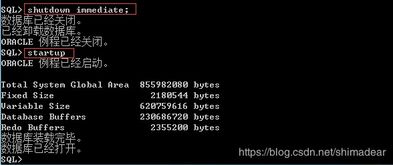
SQL> show parameter audit_trail;
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
SQL> alter system set audit_trail=none scope=spfile;
3.或者将aud$表移到另外一个表空间下,以减少system表空间的压力和被撑爆的风险。
附:11g中有关audit_trail参数的设置说明:
Syntax AUDIT_TRAIL={ none| os| db [, extended]| xml [, extended]}
AUDIT_TRAIL enables or disables database auditing.
Disables standard auditing. This value is the default if the AUDIT_TRAIL parameter was not set
in the initialization parameter file or if you created the database using a method other than
Database Configuration Assistant. If you created the database using Database Configuration
Assistant, then the default is db.
Directs all audit records to an operating system file. Oracle recommends that you use the os
setting, particularly if you are using an ultra-secure database configuration.
Directs audit records to the database audit trail(the SYS.AUD$ table), except for records
that are always written to the operating system audit trail. Use this setting for a general
If the database was started in read-only mode with AUDIT_TRAIL set to db, then Oracle Database
internally sets AUDIT_TRAIL to os. Check the alert log for details.
Performs all actions of AUDIT_TRAIL=db, and also populates the SQL bind and SQL text CLOB-type
columns of the SYS.AUD$ table, when available. These two columns are populated only when this
If the database was started in read-only mode with AUDIT_TRAIL set to db, extended, then Oracle
Database internally sets AUDIT_TRAIL to os. Check the alert log for details.
Writes to the operating system audit record file in XML format. Records all elements of the
AuditRecord node except Sql_Text and Sql_Bind to the operating system XML audit file.
Performs all actions of AUDIT_TRAIL=xml, and populates the SQL bind and SQL text CLOB-type columns
of the SYS.AUD$ table, wherever possible. These columns are populated only when this parameter
You can use the SQL AUDIT statement to set auditing options regardless of the setting of this
二、oracle 审计包括哪几种,都是什么
审计(Audit)用于监视用户所执行的数据库操作,并且Oracle会将审计跟踪结果存放到OS文件(默认位置为$ ORACLE_BASE/admin/$ORACLE_SID/adump/)或数据库(存储在system表空间中的SYS.AUD$表中,可通过视图 dba_audit_trail查看)中。默认情况下审计是没有开启的。
不管你是否打开数据库的审计功能,以下这些操作系统会强制记录:用管理员权限连接Instance;启动数据库;关闭数据库。
默认为false,当设置为true时,所有sys用户(包括以sysdba,sysoper身份登录的用户)的操作都会被记录,audit trail不会写在aud$表中,这个很好理解,如果数据库还未启动aud$不可用,那么像conn/as sysdba这样的连接信息,只能记录在其它地方。如果是windows平台,audti trail会记录在windows的事件管理中,如果是linux/unix平台则会记录在audit_file_dest参数指定的文件中。
DB:将audit trail记录在数据库的审计相关表中,如aud$,审计的结果只有连接信息;
DB,Extended:这样审计结果里面除了连接信息还包含了当时执行的具体语句;
OS:将audit trail记录在操作系统文件中,文件名由audit_file_dest参数指定;
注:这两个参数是static参数,需要重新启动数据库才能生效。
当开启审计功能后,可在三个级别对数据库进行审计:Statement(语句)、Privilege(权限)、object(对象)。
按语句来审计,比如audit table会审计数据库中所有的create table,drop table,truncate table语句,alter session by cmy会审计cmy用户所有的数据库连接。
按权限来审计,当用户使用了该权限则被审计,如执行grant select any table to a,当执行了audit select any table语句后,当用户a访问了用户b的表时(如select* from b.t)会用到select any table权限,故会被审计。注意用户是自己表的所有者,所以用户访问自己的表不会被审计。
按对象审计,只审计on关键字指定对象的相关操作,如aduit alter,delete,drop,insert on cmy.t by scott;这里会对cmy用户的t表进行审计,但同时使用了by子句,所以只会对scott用户发起的操作进行审计。注意Oracle没有提供对schema中所有对象的审计功能,只能一个一个对象审计,对于后面创建的对象,Oracle则提供on default子句来实现自动审计,比如执行audit drop on default by access;后,对于随后创建的对象的drop操作都会审计。但这个default会对之后创建的所有数据库对象有效,似乎没办法指定只对某个用户创建的对象有效,想比 trigger可以对schema的DDL进行“审计”,这个功能稍显不足。
三、如何审计Oracle数据库中表操作
修改数据库的初始化参数audit_trail,从none修改为你需要的值。
AUDIT_TRAIL={ none| os| db| db,extended| xml| xml,extended}
我们选择db值作为该参数值。使得审计功能处于打开状态,将审计记录保存在数据库sys.aud$表中。
修改初始化参数文件spfile中的此参数配置值
ALTER SYSTEM SET audit_trail=db SCOPE=SPFILE sid='*';
注意,这个参数需要数据库实例重启之后才能生效。
可以审计数据库对象的DML和DDL操作,以及查询、执行和一些系统事件如登录和退出。
DDL(CREATE, ALTER& DROP of objects)
SYSTEM EVENTS(LOGON, LOGOFF etc)
每个功能还有选项,如在每个会话还是每个访问中审计,是成功或不成功时审计。
{ sql_statement_clause| schema_object_clause| NETWORK}
[ WHENEVER [ NOT ] SUCCESSFUL ];
现在的问题是找出什么应用向表插入了记录。在应用程序的逻辑上,这个表的数据只会更新,不会插入。
因此,在审计功能打开后,使用这个下列命令审计某表的插入操作。
audit insert on table_name by access;
执行成功后,此表上每一次插入操作都会被记录在sys.aud$表中。
可以查询dba_audit_trail系统视图,该视图显示就是sys.aud$表保存的审计结果。这个表的存储空间是system,如果你需要大量长期审计某些操作,请注意维护这张表。
一般维护方法有两个,定期执行truncate操作和将表的存储表空间移植到一个新建的独立表空间上。
使用noaudit代替audit命令符就可,如noaudit insert on table_name by access;